The 7 Sources of Innovation help you to look systematically for innovative Ideas. It doesn’t matter if you
- want to start a new open source project
- are searching for interesting topic for your next thesis
- are looking for innovative business idea or
- you want to put up an effective social project.
It neither doesn’t matter, if you are looking for technical or social innovation. The point rather is to find out about demand, feasibility and timing of an innovation.
Ideas are not found by accident
To find new ideas, you are normally advised to do some creativity techniques like brainstorming or you are told to build a product for yourself. Ironically there is much advice to test your idea or business model – finding the idea in the first place is something accidental.
This approach is not systematic. It is not useful to find promising ideas for startups, open-source or social projects. It is just based on the principle: Try to generate as many ideas as you can, maybe someday there will be a useful one.
The result: There are lots people out there, that say: Ideas are worthless! The only thing that counts is execution.
Good Ideas are not worthless
I would like to contradict this claim: No, good ideas are not worthless!
We need good ideas. And to find good ideas you need to know where to look.
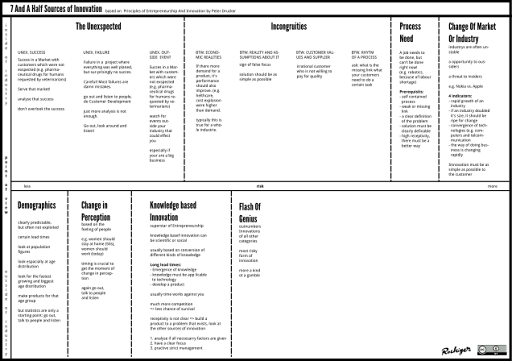
The inventor of management, Peter Drucker, detected 7 sources of innovation:
- The Unexpected
- Incongruities
- Process-Need
- Change Of Market Or Industry
- Demographics
- Change In Perception
- Knowledge-Based Innovation
Drucker chose the order of the sources not randomly:
- The risk of the sources increases.
- Innovation opportunities that lie in the sources 1 – 4 are easier discovered by insiders of an industry, opportunities that lie in the sources 5 – 7 easier by outsiders.
CC-share alike licenced. Feel free to download, if you want to share: please link back to this post.
The sources
Before we dive into the sources of innovation, keep in mind, that the sources of innovation are not mutually exclusive. Electric vehicles are a culmination of New Knowledge and Changes in Perception.
Source of Innovation: The Unexpected
Summary: Innovation often emerges from unforeseen disruptions or unexpected events that challenge the status quo and compel individuals and organizations to adapt and innovate.
Detailed Explanation: “The Unexpected” source of innovation underscores the profound notion that pioneering breakthroughs frequently stem from circumstances or events that deviate from the anticipated norm. These unanticipated occurrences serve as catalysts for fresh thinking and inventive solutions. They prompt individuals to explore uncharted territories, adapt swiftly, and unearth unconventional solutions.
Contemporary Examples:
- Post-it Notes (3M): In 1968, chemist Spencer Silver’s pursuit of a robust adhesive yielded an unexpectedly weak one. This serendipity eventually led to the iconic Post-it Notes, revolutionizing the way people communicate and share information.
- Penicillin (Alexander Fleming): In 1928, a fortuitous discovery by Alexander Fleming, a Scottish bacteriologist, of mold spores with bactericidal properties became the genesis of penicillin, the pioneering antibiotic that transformed the landscape of medicine.
- Zoom Video Conferencing: The widespread adoption of Zoom during the COVID-19 pandemic exemplifies how an unforeseen circumstance, in this case, the need for remote communication, can propel a tool into mainstream use.
Source of Innovation: Incongruities
Summary: Innovation frequently arises from recognizing discrepancies or misalignments between existing circumstances and desired outcomes.
Detailed Explanation: “Incongruities” as a source of innovation centers on the identification and harnessing of inconsistencies, contradictions, or unmet needs. When a perceptible incongruity exists between the prevailing situation and the aspired state, it serves as a potent impetus for innovation. Bridging these incongruities leads to inventive solutions that harmonize disparities.
Contemporary Examples:
- Tesla’s Electric Vehicles: Tesla’s innovative approach addressed the incongruity between environmental concerns and traditional gasoline-powered vehicles by offering high-performance electric alternatives, revolutionizing the automotive industry.
- Airbnb: Recognizing the incongruity between underutilized living spaces and travelers’ need for accommodation, Airbnb introduced a platform that effectively bridged the gap, disrupting the conventional hospitality industry.
- Smartphones: The unification of communication, photography, computing, and entertainment within a single device exemplifies the amalgamation of multiple incongruities, offering users a streamlined and multifunctional tool.
Source of Innovation: Process Need
Summary: Innovations often stem from recognizing opportunities to optimize or streamline existing processes.
Detailed Explanation: The “Process Need” source of innovation accentuates the importance of identifying prospects for refining current processes to enhance efficiency and efficacy. By identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies within the existing workflow, organizations are inspired to seek inventive solutions that ameliorate operational performance.
Contemporary Examples:
- Lean Manufacturing (Toyota): Toyota’s implementation of lean manufacturing principles ushered in a transformative era. This involved a relentless focus on process enhancement, waste reduction, quality improvement, and operational efficiency. These refinements reshaped the manufacturing landscape.
- Amazon’s Supply Chain Innovation: Amazon’s continuous innovation in supply chain and logistics operations is typified by advancements like warehouse robotics and drone delivery. These innovations optimize the supply chain, translating into swifter and more efficient services for customers.
- Lean Startup Methodology: The lean startup methodology champions rapid iteration, feedback-driven development, and the minimization of wastage in the product development process. This approach has become a cornerstone of entrepreneurial ventures, particularly in the technology sector.
Source of Innovation: Industry & Market Changes
Summary: Innovation often arises from shifts in industry and market dynamics, driven by factors such as regulatory changes, evolving consumer preferences, or shifting demographics.
Detailed Explanation: “Industry & Market Changes” as a source of innovation underscores the role of disruptions in reshaping the business landscape. Whether emanating from regulatory amendments, evolving consumer tastes, or changing demographic compositions, these shifts generate opportunities for innovative products or services. Adapting to these evolving dynamics can result in significant advances.
Contemporary Examples:
- Electric Vehicles: The automotive industry’s transformation was triggered by industry changes, including environmental regulations and heightened consumer demand for eco-friendly transportation options. This transition led to the emergence of electric vehicles, with companies like Tesla spearheading the movement.
- Plant-Based and Lab-Grown Meat: A shift in dietary preferences towards ethical and sustainable food choices has propelled the growth of plant-based and lab-grown meat products, which align with changing consumer demands.
- Telemedicine: Industry and market changes, driven by the need for remote healthcare access, catalyzed the expansion of telemedicine services, offering accessible and convenient healthcare solutions.
Source of Innovation: Demographics
Summary: Innovations can be inspired by changes in the age, size, or composition of populations, as these shifts necessitate tailored solutions.
Detailed Explanation: The “Demographics” source of innovation emphasizes the significance of understanding and addressing the distinctive needs and preferences of diverse demographic groups. As populations evolve with respect to age, size, and composition, entrepreneurial endeavors and businesses can seize opportunities by devising products and services that resonate with these evolving demographics.
Contemporary Examples:
- Baby Boomer Retirement Planning: The aging of the baby boomer generation has created a demand for tailored financial and healthcare services. Innovations in retirement planning and senior care have emerged to address this demographic shift.
- Online Learning Platforms: Online learning platforms like Coursera and edX cater to learners of all ages, offering diverse courses and programs that accommodate the varied educational needs of different demographics.
- Apps and Products for Aging Populations: The development of applications and products aimed at addressing the health, mobility, and accessibility requirements of aging populations, such as medication reminder apps and senior-friendly smartphones, is in response to demographic changes.
Source of Innovation: Changes in Perception
Summary: Innovations can originate from shifts in cultural norms, attitudes, and values, as these changing perceptions create opportunities for novel products and services.
Detailed Explanation: “Changes in Perception” as a source of innovation accentuates the dynamic nature of cultural norms, attitudes, and values. When societal perspectives undergo transformation, it paves the way for innovative products and services that align with these evolving perceptions. Recognizing and capitalizing on these shifts can lead to pioneering and impactful innovations.
Contemporary Examples:
- Plant-Based Diets: The increased acceptance of plant-based diets, driven by health and environmental concerns, has given rise to a variety of vegan and vegetarian food products that cater to the changing perception of ethical and sustainable eating.
- Eco-Friendly Products: Heightened environmental consciousness has ushered in the era of eco-friendly and sustainable products across various industries, reflecting shifting perceptions of environmental responsibility.
- Digital Art and NFTs: The art world is currently undergoing a transformation as digital art and NFTs challenge traditional notions of art ownership and value. This shift in perception has opened up new avenues for artists and collectors.
Source of Innovation: New Knowledge
Summary: Innovations often result from advances in scientific or technical knowledge, with breakthroughs and discoveries creating opportunities for revolutionary innovations.
Detailed Explanation: The “New Knowledge” source of innovation underscores the profound role of breakthroughs and advancements in scientific and technical knowledge. When researchers unlock new insights or principles, it unveils opportunities for revolutionary innovations across a spectrum of fields. The application of this fresh knowledge drives transformative change.
Contemporary Examples:
- CRISPR Gene-Editing Technology: The advent of CRISPR-Cas9, a revolutionary gene-editing technology, is a product of breakthroughs in molecular biology. Its potential to transform medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology by enabling precise gene editing exemplifies the power of new knowledge.
- Advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: Ongoing progress in AI and machine learning has resulted in innovations such as autonomous vehicles, predictive analytics, virtual assistants, and a myriad of applications across diverse industries.
- Nanotechnology in Materials Science: Innovations in nanotechnology have facilitated the creation of novel materials with unique properties. These materials find applications in electronics, medicine, and materials engineering, ushering in novel product development possibilities.
This language and style are intended to reflect the spirit and terminology of Peter Drucker, helping convey the significance and potential of these sources of innovation in the contemporary business and technological landscape.